It Was a Matter of Time: Blockchain Technology Is Being Hacked
Contents
- 1 What Is Blockchain or Blockchain Technology?
- 2 Blockchain vs Bitcoin
- 3 What Is Blockchain Exactly?
- 4 Bitcoin Blockchain
- 5 Bitcoin Blockchain Components
- 6 Blockchain Technology
- 7 First Blockchain Application
- 8 How Does Blockchain Work?
- 9 Blockchain Example
- 10 Who Writes Blocks In Blockchain?
- 11 Difficulty Settings In Bitcoin And Blockchain
- 12 It Is No Longer Infallible
- 13 How Do You Hack A Blockchain?
What Is Blockchain or Blockchain Technology?
The famous blockchain sounds like a medieval construction. But in reality it is a new type of digital accounting book and distributed to the forefront of computer science.
Blockchain vs Bitcoin
Perhaps you have heard the media describe blockchain technology as “the technology that drives Bitcoin.” Or you may have heard that large banks and companies are interested in using blockchain technology, but not Bitcoin itself… So, if the blockchain or blockchain is not Bitcoin.
What Is Blockchain Exactly?
Let’s go for start at the beginning, with the invention of the blockchain. Which is directly linked to what is Bitcoin. “Satoshi Nakomoto” is the pseudonym of the mysterious creator of this technology, whose true identity remains unknown to this day.
In 2009, Satoshi launched blockchain technology to the public under free Bitcoin software. In addition to a technical whitepaper that described the system.
The revolutionary Satoshi system allows an open computer network to create and share valuable data in an incorruptible manner … without the need of any central authority to keep the data synchronized and accurate.
For this reason, the blockchain is sometimes called “decentralized or distributed book.” It works strictly peer to peer (or peer to peer without intermediaries). Similar to file sharing systems on the internet like BitTorrent.

Bitcoin Blockchain
So, if Bitcoin operates through a public accounting book …
The bitcoin blockchain, or bitcoin blockchain, is the mechanism that keeps all participants in consensus. And avoid accounting errors, whether accidental or intentional.
Bitcoin Blockchain Components
Satoshi merged several existing technologies to create blockchain technology:
1.The decentralized network architecture is the first component.
2.The second element is asymmetric cryptography (or public key cryptography). No need for participants to share their private codes (private keys).
3.The third and final element is the proof of work hash. Which serves as proof that the required computational work was performed.
Actually Satoshi did not invent any of these technologies, but by combining them, he created the unique formula called blockchain or btc blockchain.
Blockchain Technology
Fortunately, you do not need to be an expert in each of these contributing technologies to have an overview of blockchain. You just have to know that they are important gears in the digital machinery of the blockchain.
First Blockchain Application
The first application of blockchain technology was of course monetary. The creation of a fully secure online accounting book that tracks the ownership of the “digital gold” known as Bitcoin.
In the future, blockchain technology is likely to be the way society tracks properties of all kinds, such as:
- Actions
- bonuses
- propeti writhing’s
- even legal contracts …
Since this technology has enormous disruptive potential in a large number of industries. In fact, there are many initiatives exploring different blockchain applications in different industries.
But for now let’s focus only on Bitcoin and its monetary application …
How is the Bitcoin blockchain in a public anti-fraud registry that faithfully records transactions without any central control entity that keeps its participants honest?
How Does Blockchain Work?
You may have heard about Bitcoin miners, if not… Check out our video, “ What is mining Bitcoins? ”Which easily explains how mining works on the Bitcoin network.
But in summary, basically the miners record all Bitcoin transactions in data packets known as “blocks.”
These blocks are linked in a linear sequence using a special code. Each transaction in a block enters into the formation of this code … And the final result is recorded in that block.
Then the next block forms a new code and includes the code from the previous block and so on. The chaining of all the blocks together guarantees the permanence of the previous transactions … You cannot change the information of the previous blocks without also changing all the subsequent blocks.
Together, these linked blocks form a growing public record with all Bitcoin transactions since its inception … Known of course as the blockchain or blockchain.
Blockchain Example
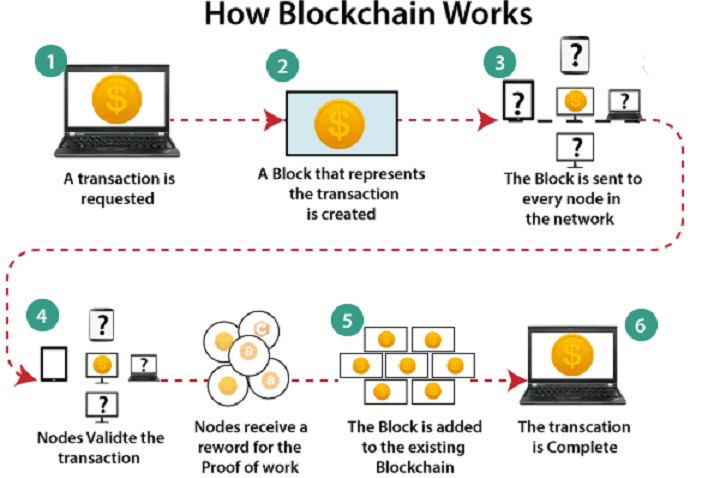
Now that the term makes a little more sense, I will explain the blockchain in greater depth. Imagine this example:
Let’s say you send some bitcoins to a friend using a Bitcoin wallet , your transaction will be retransmitted across the entire Bitcoin network.
Everyone will see that address A (your address) is trying to send that amount of coins to address B , (your friend’s address).
People who operate the so-called “complete nodes,” that is, Bitcoin software clients that store the entire blockchain … will quickly receive information about your transaction.
Full nodes verify your transaction information against their own stored copy of the blockchain. Therefore, the full nodes check whether the address A has enough Bitcoins to pay the specified amount to the direction B .
They will also check other new transactions. To verify that A is not trying to send the same currencies simultaneously to address B and also C or to addresses C, D, E and so on.
This particular form of fraud is known as a “double expense.”
It is important to note that double spending was a major technical problem in computing … Since it prevented the reliability of peer to peer electronic money (or peer to peer without intermediaries). Until Satoshi’s blockchain solution appeared.
Who Writes Blocks In Blockchain?
Double spending aside, let’s return to our example:
If your transaction is approved by complete nodes, it will soon be transmitted to a special type of complete node. Although sometimes your transaction will reach this special node first.
These special types of complete nodes have the ability to register transaction blocks in the blockchain … Guess what these special nodes are called? These are the famous “miners” of Bitcoin.
Blockchain like Bitcoin, in which miners compete to write the next block in exchange for a reward … It is the type known as “Proof of Work” blockchains.
The work in question refers to the hash or resolution of a mathematical equation. Which reduces information of any length to a fixed length.
Difficulty Settings In Bitcoin And Blockchain
The Bitcoin protocol adjusts the difficulty of this equation periodically and automatically. To satisfy the amount of computing power available in the network for its solution.
These difficulty settings ensure that a new block is written every ten minutes on average. No matter if more miners enter or leave the Bitcoin network.
At the beginning of Bitcoin the difficulty was low. And the blocks could be solved reliably using only a laptop. As the value of Bitcoin increased, so did the difficulty of mining. Since this became increasingly competitive.
Today, mining is done with specialized hardware. Hosted and refrigerated in huge data centers or mining farms like this one:
It Is No Longer Infallible
In total, hackers have stolen almost $2 billion in cryptocurrencies since the beginning of 2017, mostly at exchange sites, and that is what has been publicly disclosed. These are not just solitary opportunistic attackers, much less: it is presumed that there is a whole structure behind.
We shouldn’t be surprised. Blockchains are particularly attractive to robbery because fraudulent transactions cannot be reversed as they can often be in the traditional financial system.
On top of that, we have known for a long time that just as blockchains have unique security features, they have unique vulnerabilities that they were a matter of time before they were left at the mercy of the friends of others.
How Do You Hack A Blockchain?
A blockchain is a cryptographic database maintained by a network of computers, each of which stores a copy of the most updated version. A blockchain protocol is a set of formulas that dictates how computers on the network, called nodes, should verify new transactions and add them to the database.
The protocol uses cryptography, game and economics theory to create incentives for nodes to work to secure the network instead of attacking it for personal gain. If configured correctly, this system can make it extremely difficult and expensive to add fake transactions, but relatively easy to verify valid ones.
But the more complex a blockchain system is, the more ways there are to make mistakes when configuring it. Earlier this month, the company in charge of Zcash – a cryptocurrency that uses extremely complicated mathematics to allow to clients make transactions in private – revealed that it had secretly fixed a “subtle cryptographic defect” that had been accidentally incorporated into the protocol. An attacker could have exploited it to make an unlimited counterfeit Zcash. Fortunately, nobody seems to have done that.
So, in theory, the way to attack a blockchain protocol depends on having made mistakes to program it, but it also has to be a very lucrative robbery because renting enough data-mining equipment to attack, for example, bitcoin, costs around $ 260,000 per hour. If it is not successful, it is lost money.
By mid-2018, the attackers began launching 51% attacks against a series of relatively small and slightly traded currencies, such as Verge, Monacoin and Bitcoin Gold and stole an estimated total of US $ 20 million. Months ago, hackers stole around $ 100,000 using a series of attacks on a currency called Vertcoin. The blow against Ethereum Classic, which raised more than the US $ 1 million, was the first against one of the top 20 currencies.
References.
https://www.technologyreview.com/s/612974/once-hailed-as-unhackable-blockchains-are-now-getting-hacked/
https://yro.slashdot.org/story/19/02/22/2239210/once-hailed-as-unhackable-blockchains-are-now-getting-hacked
https://www.reddit.com/r/technology/comments/at1svv/once_hailed_as_unhackable_blockchains_are_now/




